Introduction: Pain is an inevitable part of the human experience, but living with chronic pain can be debilitating, affecting every aspect of one’s life. Whether it’s a dull ache or a sharp, stabbing sensation, pain can interfere with daily activities, disrupt sleep and dampen overall quality of life. Fortunately, there are various strategies and treatments available to help manage and alleviate pain, allowing individuals to regain control and live more comfortably.
Understanding Pain:
Before diving into pain relief strategies, it’s essential to understand what pain is and how it works. Pain is a complex sensation involving both physical and emotional components. It serves as a warning sign that something is wrong in the body, prompting us to take action to protect ourselves from further harm. However, chronic pain, which persists long after the initial injury or illness has healed, can be challenging to manage and often requires a multifaceted approach.
Natural Remedies:
For those seeking natural alternatives to traditional pain medications, several options may provide relief. These include:
- Exercise: Regular physical activity releases endorphins, the body’s natural painkillers and helps improve overall mood and well-being.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
- Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs and supplements, such as turmeric, ginger and omega-3 fatty acids, have anti-inflammatory properties and may help alleviate pain.
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese therapy involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and relieve pain.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices like yoga, meditation and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, easing the perception of pain.
Over-the-Counter Medications:
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers are readily available and can be effective for mild to moderate pain. Common OTC options include:
- Acetaminophen: This medication relieves pain and reduces fever but does not have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen sodium are NSAIDs that help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. However, long-term use can lead to stomach ulcers and other complications, so it’s essential to use them sparingly and as directed.
Prescription Medications:
For more severe or chronic pain, prescription medications may be necessary. These include:
- Opioids: Powerful painkillers like oxycodone, hydrocodone and morphine are often prescribed for severe pain. However, they carry a risk of addiction and overdose and should only be used under close medical supervision.
- Antidepressants and Anticonvulsants: Certain antidepressant and anticonvulsant medications can help alleviate chronic pain by affecting the way pain signals are processed in the brain.
- Muscle Relaxants: These medications help relax tense muscles and relieve associated pain, especially in conditions like fibromyalgia and muscle spasms.
Alternative Therapies:
In addition to medication, various alternative therapies can complement traditional treatments and provide additional pain relief. These include:
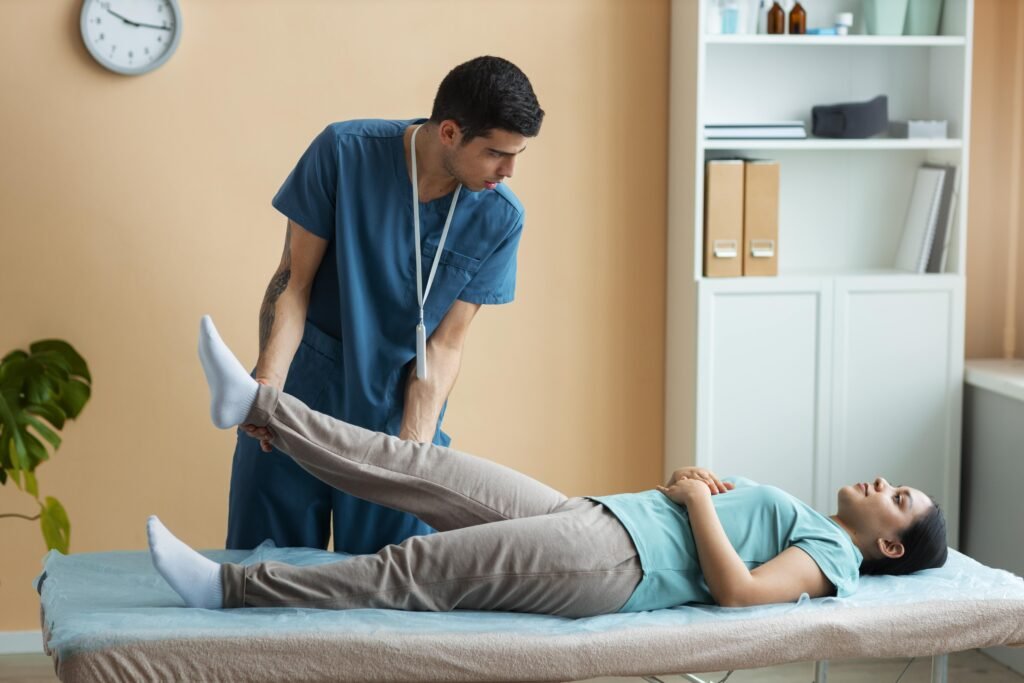
- Physical Therapy: A customized exercise and stretching program can help improve flexibility, strength and mobility, reducing pain and preventing future injuries.
- Chiropractic Care: Spinal manipulation and adjustments performed by chiropractors can help alleviate pain caused by misalignments or imbalances in the spine.
- Massage Therapy: Massage techniques like deep tissue massage and trigger point therapy can help relax muscles, improve circulation and reduce pain and tension.
- Biofeedback: This technique teaches individuals to control bodily functions like heart rate and muscle tension to reduce pain and stress levels.
Lifestyle Changes:
Making certain lifestyle modifications can also play a significant role in pain management. These include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can put added strain on the joints and exacerbate pain, so maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial.
- Improving Posture: Practicing good posture can help prevent and alleviate pain in the back, neck and shoulders by reducing strain on the muscles and joints.
- Getting Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep can worsen pain perception and make it harder to cope with discomfort, so prioritizing good sleep hygiene is essential.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate pain and interfere with the body’s ability to heal, so finding healthy coping mechanisms like meditation, journaling or spending time in nature is important.
Conclusion: Living with chronic pain can be challenging, but it’s essential to remember that relief is possible. By exploring various treatment options, including natural remedies, medications, alternative therapies and lifestyle changes, individuals can find a personalized approach to pain management that works for them. Whether it’s through exercise, medication, acupuncture or a combination of strategies, taking proactive steps to address pain can lead to improved quality of life and greater overall well-being. Remember, pain relief is not a one-size-fits-all solution, so don’t hesitate to consult with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive pain management plan tailored to your needs and preferences. **


